Learn about it
Find out the benefits and the potential impact screen time can have on your child and insights from parents, children and experts on the issue.
Find out the benefits and the potential impact screen time can have on your child and insights from parents, children and experts on the issue.


One in three Internet users online worldwide is under 18 according to UNICEF report

41% of parents of 12-15s find it hard to control their child’s screen time according to the latest Ofcom Children and Parents: Media use and attitudes report 2017

According to Oxford University research of 20,000 parents of children aged between 2 and 5 screen time limits may have nothing to do with a young child’s ability to thrive
Taking a step back and looking at research as a whole, the impact of screen time’s on children’s wellbeing is still being debated, however, now more and more experts suggest that we should focus more on what children are doing online and less on how long they are online.
Get expert advice on how to get the best out of screen time for your child over the summer holidays
Read article![]()
Download our full guide to help your child get the best from their screen time.
Young people recognise the positive role of the internet in relation to self-expression, developing understanding, bringing people together and respecting and celebrating differences.
As children get older social media takes centre stage particularly as they make the transition from primary to secondary school.
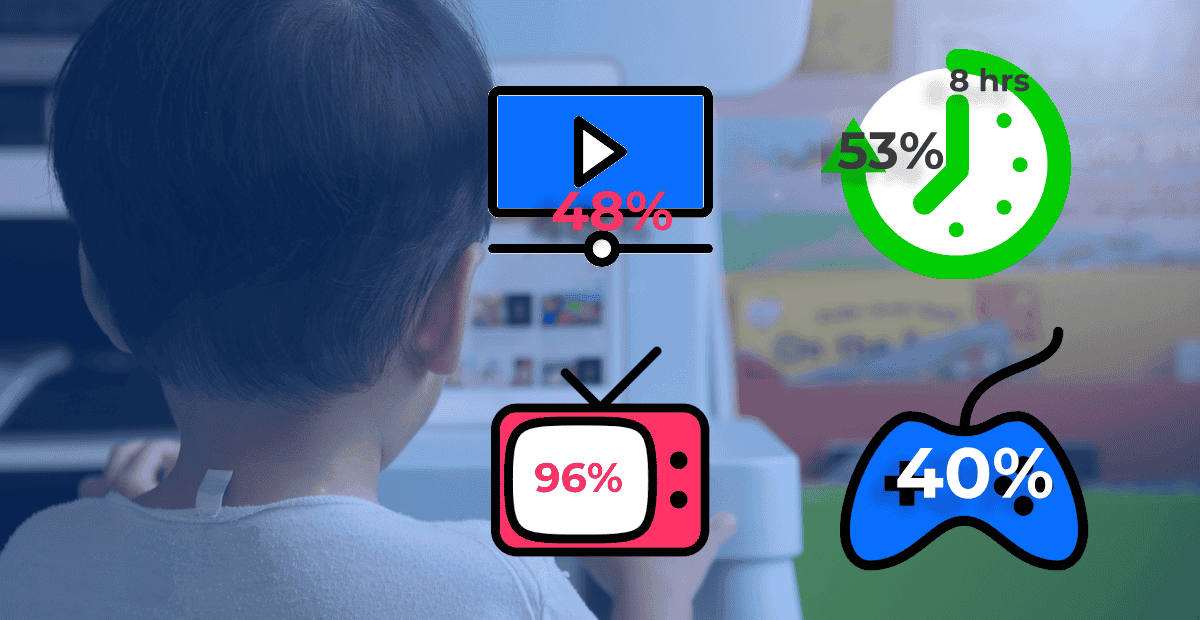
According to Ofcom research children listed the following as their top concerns:
Parents highlight the following concerns about the potential of harm the online world can expose their children to:
Source: Parenting Digital Natives (2018)
Although two-thirds of 12-15s (67%) agree that they have a good balance between screen time and doing other things, and more than half of 12-15s disagree that they find it hard to control their screen time (53%).
“…rather than worrying about the catch-all notion of ‘screen time’ it might be better to focus on whether, when and why particular digital activities help or harm individual children.”
Source: Sonia Livingstone
The idea of screen time as a one-dimensional activity is changing -The Common Sense Census: Media Use by Tweens and Teens identifies four main categories of screen time.
Source: Common Sense Media
Ofcom stats of what they are doing – children are doing different things when they are in front of a screen:
See more articles and resources to help children stay safe online.